Hard Numbers
Hard Numbers: Israel assassinates Hezbollah commander, DOGE gets DOGE’d, Ethiopian volcano erupts, Not much to show for COP30
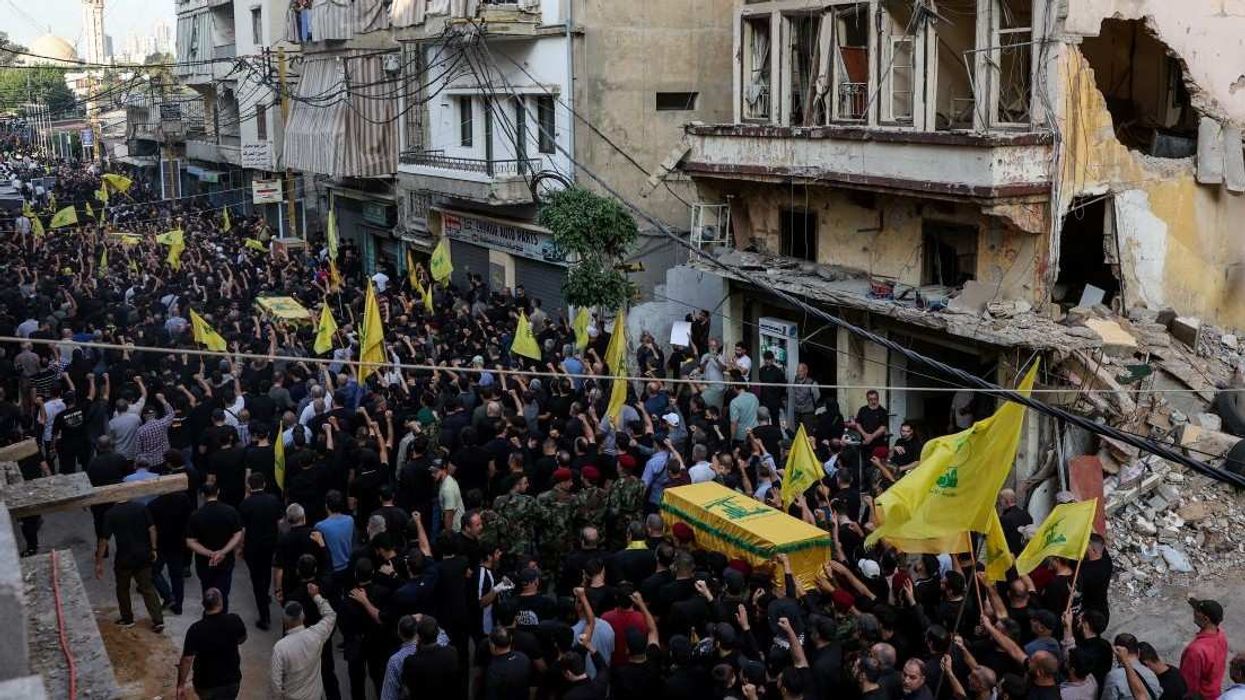
The Israeli military assassinated a senior Hezbollah commander in an airstrike on the Lebanese capital of Beirut on Sunday. The attack killed at least five people overall.
Nov 24, 2025