Closing the Gap
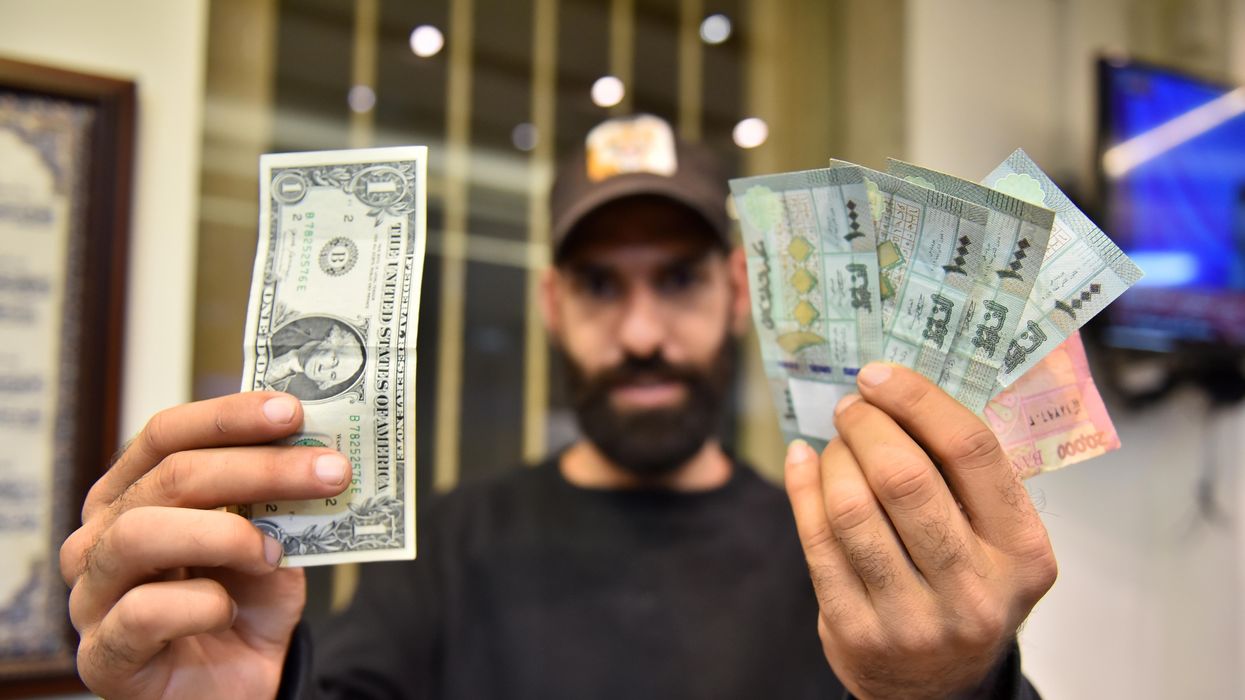
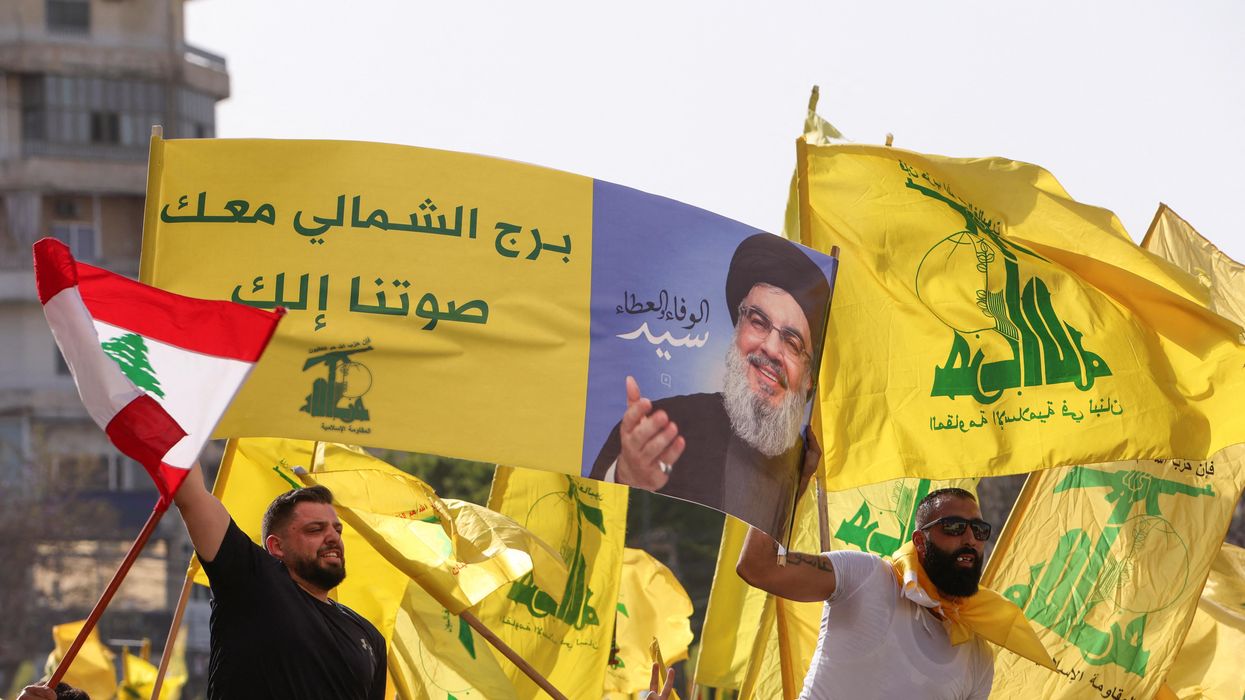
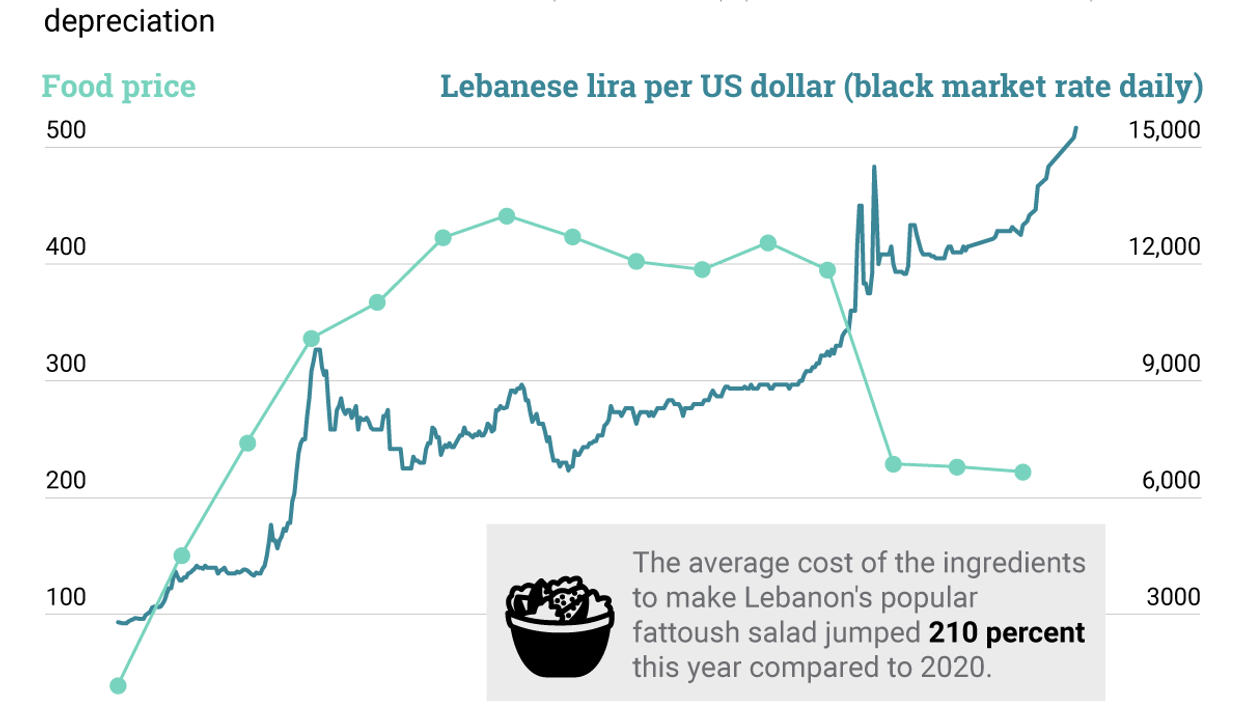
What We’re Watching: Digital payment lifelines for cash-strapped Lebanon, digital solutions for overcoming COVID, fintech & the war in Ukraine
Digital payment lifelines for cash-strapped Lebanon; digital solutions for overcoming COVID; fintech & the war in Ukraine.
Oct 07, 2022