Science & Tech
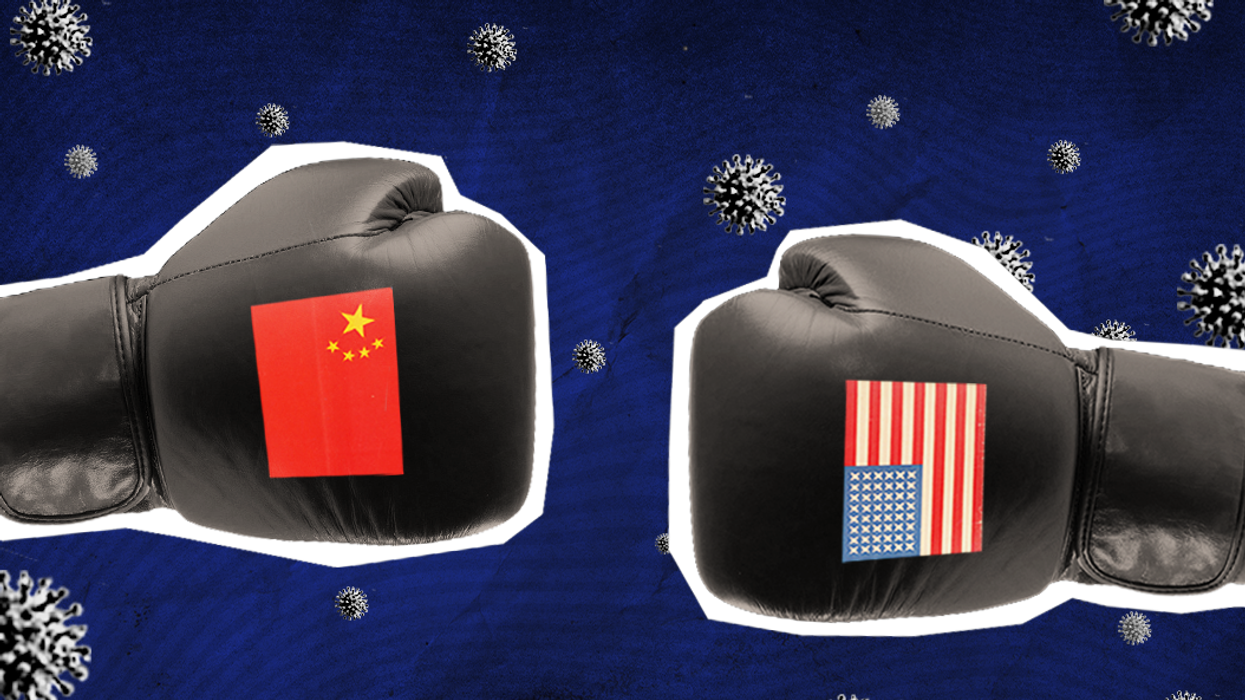
US-China tech tensions: the impact on the global digital landscape
As the digital world continues to grow and evolve, there still exists a digital divide between the US and China. Alexis Serfaty, director of geotechnology at Eurasia Group, in a GZERO livestream presented by Visa, says that has long as US-China relations continue to be involved in a “tech cold war,” other countries, especially in developed regions, may find themselves compelled to take sides when it comes to adopting new technology infrastructure and standards.
Oct 02, 2023