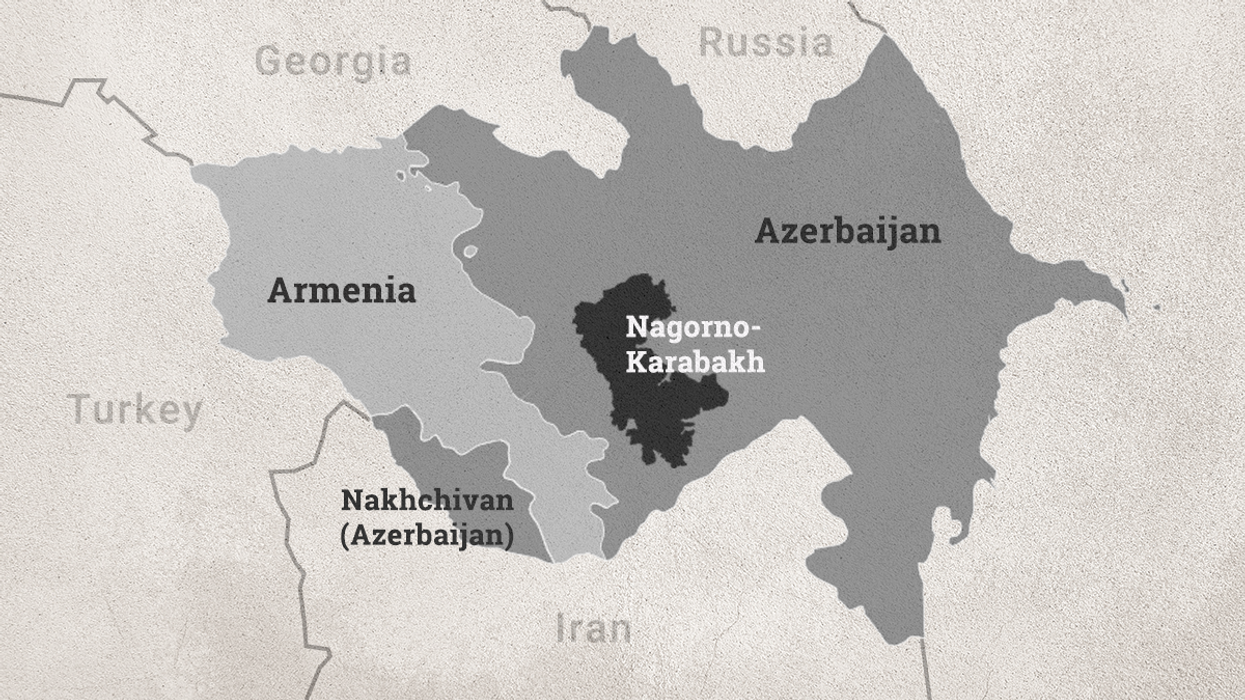
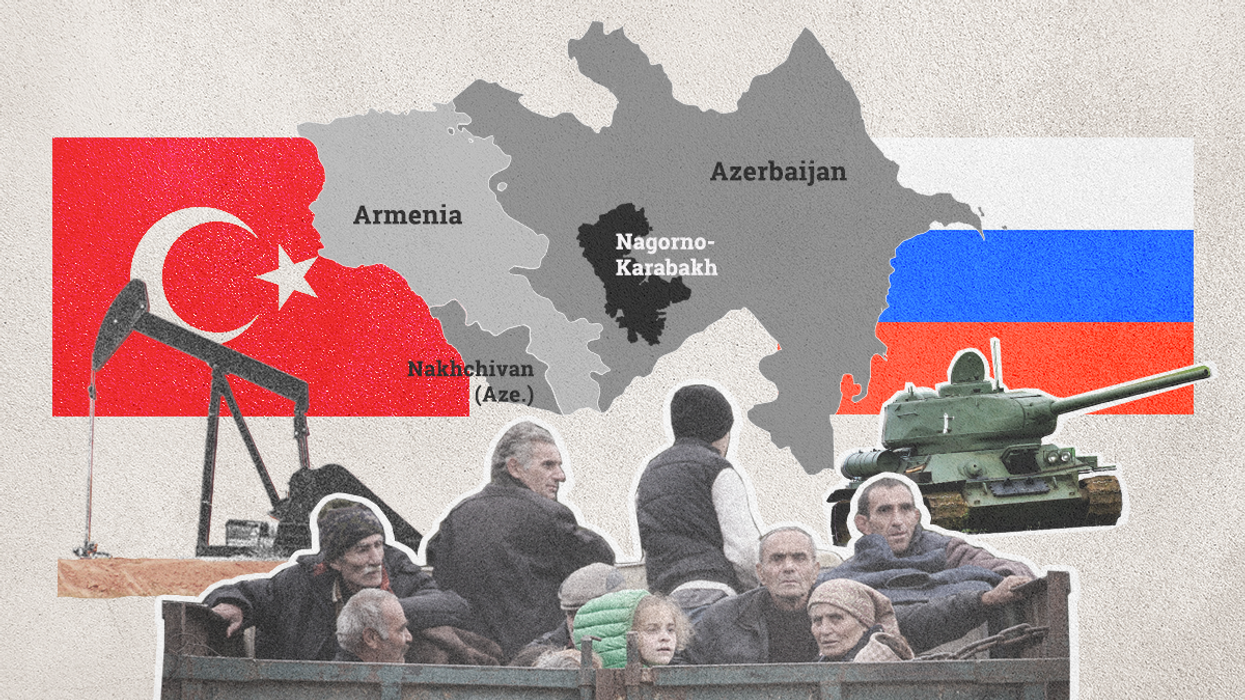
Analysis
Five stories to be thankful for
Although not all of our global readers celebrate Thanksgiving, it’s still good to remind ourselves that while the world offers plenty of fodder for doomscrolling and despair, there are still lots of things to be grateful for too.
Nov 26, 2025